Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The first reported hepatitis E outbreak in a food manufacturing factory: Korea, 2022
- Hansol Yeom, Soonryu Seo, Youngsil Yoon, Jaeeun Lee, Myung-Guk Han, Deog-Yong Lee, Sun-Whan Park, Song A Park, Sook-Hyang Jeong, Jin Gwack
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2023;14(1):15-22. Published online February 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2022.0305
- 1,663 View
- 139 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF 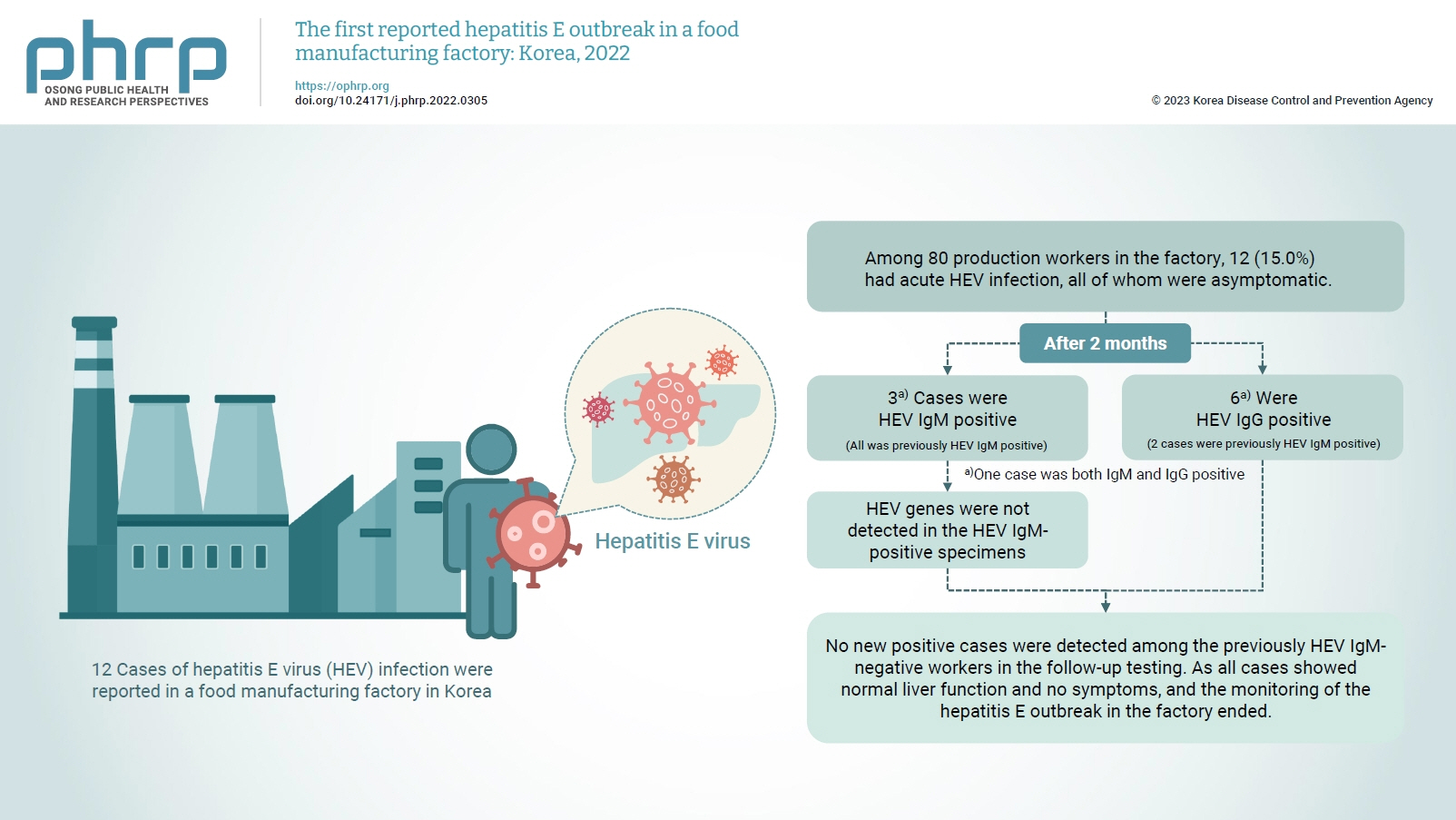
- Objectives
On February 16, 2022, 12 cases of hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection were reported in a food manufacturing factory in Korea. The aim of this study was to identify additional cases and to determine the source of this HEV outbreak. Methods: This study was an in-depth investigation of 12 HEV immunoglobulin M (IgM)-positive cases and their demographic, clinical, and epidemiological characteristics. On-site specimens were collected from the environment and from humans, and a follow-up investigation was conducted 2 to 3 months after the outbreak. Results: Among 80 production workers in the factory, 12 (15.0%) had acute HEV infection, all of whom were asymptomatic. The follow-up investigation showed that 3 cases were HEV IgMpositive, while 6 were HEV IgG-positive. HEV genes were not detected in the HEV IgM-positive specimens. HEV genes were not detected in the food products or environmental specimens collected on-site. HEV was presumed to be the causative pathogen. However, it could not be confirmed that the source of infection was common consumption inside the factory. Conclusion: This was the first domestic case of an HEV infection outbreak in a food manufacturing factory in Korea. Our results provide information for the future control of outbreaks and for the preparation of measures to prevent domestic outbreaks of HEV infection.
- The laboratory test procedure to confirm rotavirus vaccine infection in severe complex immunodeficiency patients
- Su-Jin Chae, Seung-Rye Cho, Wooyoung Choi, Myung-Guk Han, Deog-Yong Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2021;12(4):269-273. Published online August 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2021.0079
- 4,627 View
- 87 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - The rotavirus vaccine is a live vaccine, and there is a possibility of infection by the virus strain used in the vaccine. We investigated the process of determining whether an infection was caused by the vaccine strain in a severe complex immunodeficiency (SCID) patient with rotavirus infection. The patient was vaccinated with RotaTeq prior to being diagnosed with SCID. The testing process was conducted in the following order: confirming rotavirus infection, determining its genotype, and confirming the vaccine strain. Rotavirus infection was confirmed through enzyme immunoassay and VP6 gene detection. G1 and P[8] were identified by multiplex polymerase chain reaction for the genotype, and G3 was further identified using a single primer. By detecting the fingerprint gene (WC3) of RotaTeq, it was confirmed that the detected virus was the vaccine strain. Genotypes G1 and P[8] were identified, and the infection was suspected of having been caused by rotavirus G1P[8]. G1P[8] is the most commonly detected genotype worldwide and is not included in the recombinant strains used in vaccines. Therefore, the infection was confirmed to have been caused by the vaccine strain by analyzing the genetic relationship between VP4 and VP7. Rotavirus infection by the vaccine strain can be identified through genotyping and fingerprint gene detection. However, genetic linkage analysis will also help to identify vaccine strains.
- Detection of Novel Coronavirus on the Surface of Environmental Materials Contaminated by COVID-19 Patients in the Republic of Korea
- Sang-Eun Lee, Deog-Yong Lee, Wook-Gyo Lee, ByeongHak Kang, Yoon Suk Jang, Boyeong Ryu, SeungJae Lee, Hyunjung Bahk, Eungyu Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2020;11(3):128-132. Published online May 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2020.11.3.03
- 8,861 View
- 281 Download
- 45 Web of Science
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF This study aimed to determine the presence of SARS-CoV-2 on surfaces frequently touched by COVID-19 patients, and assess the scope of contamination and transmissibility in facilities where the outbreaks occurred. In the course of this epidemiological investigation, a total of 80 environmental specimens were collected from 6 hospitals (68 specimens) and 2 “mass facilities” (6 specimens from a rehabilitation center and 6 specimens from an apartment building complex). Specific reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction targeting of RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, and envelope genes, were used to identify the presence of this novel coronavirus. The 68 specimens from 6 hospitals (A, B, C, D, E, and G), where prior disinfection/cleaning had been performed before environmental sampling, tested negative for SARS-CoV-2. However, 2 out of 12 specimens (16.7%) from 2 “mass facilities” (F and H), where prior disinfection/cleaning had not taken place, were positive for SARS-CoV-2 RNA polymerase, and envelope genes. These results suggest that prompt disinfection and cleaning of potentially contaminated surfaces is an effective infection control measure. By inactivating SARS-CoV-2 with disinfection/cleaning the infectivity and transmission of the virus is blocked. This investigation of environmental sampling may help in the understanding of risk assessment of the COVID-19 outbreak in “mass facilities” and provide guidance in using effective disinfectants on contaminated surfaces.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing the impact of architectural and behavioral interventions for controlling indoor COVID-19 infection risk: An agent-based approach
Anxiao Zhang, Qi Zhen, Chi Zheng, Jing Li, Yue Zheng, Yiming Du, Qiong Huang, Qi Zhang
Journal of Building Engineering.2023; 74: 106807. CrossRef - Advancements in COVID-19 Testing: An In-depth Overview
Rajesh Kumar, Seetha Harilal, Abdullah G. Al-Sehemi, Mehboobali Pannipara, Githa Elizabeth Mathew, Bijo Mathew
Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology.2023; 24(9): 1122. CrossRef - Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) research agenda for healthcare epidemiology
Lona Mody, Ibukunoluwa C. Akinboyo, Hilary M. Babcock, Werner E. Bischoff, Vincent Chi-Chung Cheng, Kathleen Chiotos, Kimberly C. Claeys, K. C. Coffey, Daniel J. Diekema, Curtis J. Donskey, Katherine D. Ellingson, Heather M. Gilmartin, Shruti K. Gohil, An
Infection Control & Hospital Epidemiology.2022; 43(2): 156. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 on Surfaces and HVAC Filters in Dormitory Rooms
Jin Pan, Seth A. Hawks, Aaron J. Prussin, Nisha K. Duggal, Linsey C. Marr
Environmental Science & Technology Letters.2022; 9(1): 71. CrossRef - COVID-19 Cluster Linked to Aerosol Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via Floor Drains
Taewon Han, Heedo Park, Yungje Jeong, Jungmin Lee, Eungyeong Shon, Man-Seong Park, Minki Sung
The Journal of Infectious Diseases.2022; 225(9): 1554. CrossRef - Environmental Contamination with SARS-CoV-2 in Hospital COVID Department: Antigen Test, Real-Time RT-PCR and Virus Isolation
Urška Rozman, Lea Knez, Goran Novak, Jernej Golob, Anita Pulko, Mojca Cimerman, Matjaž Ocepek, Urška Kuhar, Sonja Šostar Turk
COVID.2022; 2(8): 1050. CrossRef - Using Environmental Sampling to Enable Zoonotic Pandemic Preparedness
Avirup Sanyal, Sanskriti Agarwal, Uma Ramakrishnan, Kritika M. Garg, Balaji Chattopadhyay
Journal of the Indian Institute of Science.2022; 102(2): 711. CrossRef - Anforderungen an die Hygiene bei der Reinigung und Desinfektion von Flächen
Bundesgesundheitsblatt - Gesundheitsforschung - Ge.2022; 65(10): 1074. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: a review of molecular diagnostic tools including sample collection and commercial response with associated advantages and limitations
Harikrishnan Jayamohan, Christopher J. Lambert, Himanshu J. Sant, Alexander Jafek, Dhruv Patel, Haidong Feng, Michael Beeman, Tawsif Mahmood, Ugochukwu Nze, Bruce K. Gale
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.2021; 413(1): 49. CrossRef - Contamination of inert surfaces by SARS-CoV-2: Persistence, stability and infectivity. A review
Montse Marquès, José L. Domingo
Environmental Research.2021; 193: 110559. CrossRef - A Systematic Review of Surface Contamination, Stability, and Disinfection Data on SARS-CoV-2 (Through July 10, 2020)
Noah Bedrosian, Elizabeth Mitchell, Elsa Rohm, Miguel Rothe, Christine Kelly, Gabrielle String, Daniele Lantagne
Environmental Science & Technology.2021; 55(7): 4162. CrossRef - Transmission of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 via Contaminated Surfaces: What Is to Be Done?
Craig S Conover
Clinical Infectious Diseases.2021; 72(11): 2062. CrossRef - Investigation of SARS CoV-2 virus in environmental surface
Abdollah Dargahi, Farhad Jeddi, Mehdi Vosoughi, Chiman Karami, Aidin Hadisi, S. Ahamad Mokhtari, Hasan Ghobadi, Morteza Alighadri, Somayeh Biparva Haghighi, Hadi Sadeghi
Environmental Research.2021; 195: 110765. CrossRef - Ist die Desinfektion öffentlicher Flächen zur Prävention von SARS-CoV-2 – infektionen sinnvoll?
Günter Kampf, Lutz Jatzwauk
Das Gesundheitswesen.2021; 83(03): 180. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 Detection Rates from Surface Samples Do Not Implicate Public Surfaces as Relevant Sources for Transmission
Günter Kampf, Stephanie Pfaender, Emanuel Goldman, Eike Steinmann
Hygiene.2021; 1(1): 24. CrossRef - The SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) pandemic in hospital: An insight into environmental surfaces contamination, disinfectants’ efficiency, and estimation of plastic waste production
Faezeh seif, Zahra Noorimotlagh, Seyyed Abbas Mirzaee, Mojtaba Kalantar, Barat Barati, Mahdi Emamian Fard, Nozar Kalantar Fard
Environmental Research.2021; 202: 111809. CrossRef - Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA on inanimate surfaces: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Simone Belluco, Marzia Mancin, Filippo Marzoli, Alessio Bortolami, Eva Mazzetto, Alessandra Pezzuto, Michela Favretti, Calogero Terregino, Francesco Bonfante, Roberto Piro
European Journal of Epidemiology.2021; 36(7): 685. CrossRef - Management following the first confirmed case of SARS-CoV-2 in a domestic cat associated with a massive outbreak in South Korea
Taewon Han, Boyeong Ryu, Suyeon Lee, Yugyeong Song, Yoongje Jeong, Ilhwan Kim, Jeongmin Kim, Eunjin Kim, Wonjun Lee, Hyunju Lee, Haekyoung Hwang
One Health.2021; 13: 100328. CrossRef - Non-Respiratory Droplet Transmission of COVID-19 in the Isolation Ward of a Secondary Hospital in Oman
Zayid K. Al Mayahi, Nawal Al Kindi, Nasser Al Shaqsi, Noaman Al Hattali, Azza Al Hattali, Khalid Salim, Mark Beatty
Infectious Diseases in Clinical Practice.2021; 29(6): e371. CrossRef - Effectiveness of antiviral metal and metal oxide thin-film coatings against human coronavirus 229E
Louis-Vincent Delumeau, Hatameh Asgarimoghaddam, Tamiru Alkie, Alexander James Bryan Jones, Samantha Lum, Kissan Mistry, Marc G. Aucoin, Stephanie DeWitte-Orr, Kevin P. Musselman
APL Materials.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Rapid Review of SARS-CoV-1 and SARS-CoV-2 Viability, Susceptibility to Treatment, and the Disinfection and Reuse of PPE, Particularly Filtering Facepiece Respirators
José G. B. Derraik, William A. Anderson, Elizabeth A. Connelly, Yvonne C. Anderson
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2020; 17(17): 6117. CrossRef - Potential sources, modes of transmission and effectiveness of prevention measures against SARS-CoV-2
G. Kampf, Y. Brüggemann, H.E.J. Kaba, J. Steinmann, S. Pfaender, S. Scheithauer, E. Steinmann
Journal of Hospital Infection.2020; 106(4): 678. CrossRef
- Assessing the impact of architectural and behavioral interventions for controlling indoor COVID-19 infection risk: An agent-based approach
- Emergence of Norovirus GII.17-associated Outbreak and Sporadic Cases in Korea from 2014 to 2015
- Sunyoung Jung, Bo-Mi Hwang, HyunJu Jung, GyungTae Chung, Cheon-Kwon Yoo, Deog-Yong Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2017;8(1):86-90. Published online February 28, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.24171/j.phrp.2017.8.1.12
- 3,991 View
- 27 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Human norovirus are major causative agent of nonbacterial acute gastroenteritis. In general, genogroup (G) II.4 is the most prominent major genotype that circulate in human population and the environment. However, a shift in genotypic trends was observed in Korea in December 2014. In this study, we investigated the trend of norovirus genotype in detail using the database of Acute Diarrhea Laboratory Surveillance (K-EnterNet) in Korea. GII.17 has since become a major contributor to outbreaks of norovirus-related infections and sporadic cases in Korea, although the reason for this shift remain unknown.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Monitoring of foodborne viruses in pre- and post-washed root vegetables in the Republic of Korea
Sunho Park, Md Iqbal Hossain, Soontag Jung, Zhaoqi Wang, Daseul Yeo, Seoyoung Woo, Yeeun Seo, Myeong-In Jeong, Changsun Choi
Food Control.2023; 154: 109982. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Norovirus Outbreaks Reported to the Public Health Emergency Event Surveillance System, China, 2014–2017
Yiyao Lian, Shuyu Wu, Li Luo, Bin Lv, Qiaohong Liao, Zhongjie Li, Jeanette J. Rainey, Aron J. Hall, Lu Ran
Viruses.2019; 11(4): 342. CrossRef - Nearly Complete Genome Sequence of a Human Norovirus GII.P17-GII.17 Strain Isolated from Brazil in 2015
Cristina Santiso-Bellón, Azahara Fuentes-Trillo, Juliana da Silva Ribeiro de Andrade, Carolina Monzó, Susana Vila-Vicent, Roberto Gozalbo Rovira, Javier Buesa, Felipe J. Chaves, Marize Pereira Miagostovich, Jesús Rodríguez-Díaz, Jelle Matthijnssens
Microbiology Resource Announcements.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of SNP Markers for Norovirus Related FUT2 Gene in Oyster
守泉 闫
Hans Journal of Biomedicine.2019; 09(03): 135. CrossRef - Research on the contamination levels of norovirus in food facilities using groundwater in South Korea, 2015–2016
Jeong Su Lee, In Sun Joo, Si Yeon Ju, Min Hee Jeong, Yun-Hee Song, Hyo Sun Kwak
International Journal of Food Microbiology.2018; 280: 35. CrossRef - Norovirus GII.17 Associated with a Foodborne Acute Gastroenteritis Outbreak in Brazil, 2016
Juliana da Silva Ribeiro de Andrade, Tulio Machado Fumian, José Paulo Gagliardi Leite, Matheus Ribeiro de Assis, Alexandre Madi Fialho, Sergio Mouta, Cristiane Mendes Pereira Santiago, Marize Pereira Miagostovich
Food and Environmental Virology.2018; 10(2): 212. CrossRef - Phylogenetic characterization of norovirus strains detected from sporadic gastroenteritis in Seoul during 2014–2016
Young Eun Kim, Miok Song, Jaein Lee, Hyun Jung Seung, Eun-Young Kwon, Jinkyung Yu, Youngok Hwang, Taeho Yoon, Tae Jun Park, In Kyoung Lim
Gut Pathogens.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The prevalence of non-GII.4 norovirus genotypes in acute gastroenteritis outbreaks in Jinan, China
Lanzheng Liu, Hengyun Guan, Ying Zhang, Chunrong Wang, Guoliang Yang, Shiman Ruan, Huailong Zhao, Xiuyun Han, Adriana Calderaro
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(12): e0209245. CrossRef
- Monitoring of foodborne viruses in pre- and post-washed root vegetables in the Republic of Korea
- Occurrence of Norovirus GII.4 Sydney Variant-related Outbreaks in Korea
- Sunyoung Jung, Bo-Mi Hwang, Hyun Ju Jeong, Gyung Tae Chung, Cheon-Kwon Yoo, Yeon-Ho Kang, Deog-Yong Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(5):322-326. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.10.004
- 2,903 View
- 17 Download
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Human noroviruses are major causative agents of food and waterborne outbreaks of nonbacterial acute gastroenteritis. In this study, we report the epidemiological features of three outbreak cases of norovirus in Korea, and we describe the clinical symptoms and distribution of the causative genotypes. The incidence rates of the three outbreaks were 16.24% (326/2,007), 4.1% (27/656), and 16.8% (36/214), respectively. The patients in these three outbreaks were affected by acute gastroenteritis. These schools were provided unheated food from the same manufacturing company. Two genotypes (GII.3 and GII.4) of the norovirus were detected in these cases. Among them, major causative strains of GII.4 (Hu-jeju-47-2007KR-like) were identified in patients, food handlers, and groundwater from the manufacturing company of the unheated food. In the GII.4 (Hu-jeju-47-2007KR-like) strain of the norovirus, the nucleotide sequences were identical and identified as the GII.4 Sydney variant. Our data suggests that the combined epidemiological and laboratory results were closely related, and the causative pathogen was the GII.4 Sydney variant strain from contaminated groundwater.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review and meta-analysis indicates a substantial burden of human noroviruses in shellfish worldwide, with GII.4 and GII.2 being the predominant genotypes
Yijing Li, Liang Xue, Junshan Gao, Weicheng Cai, Zilei Zhang, Luobing Meng, Shuidi Miao, Xiaojing Hong, Mingfang Xu, Qingping Wu, Jumei Zhang
Food Microbiology.2023; 109: 104140. CrossRef - Molecular epidemiology of norovirus infections in children with acute gastroenteritis in 2017–2019 in Tianjin, China
Yulian Fang, Yanzhi Zhang, Hong Wang, Ouyan Shi, Wei Wang, Mengzhu Hou, Lu Wang, Jinying Wu, Yu Zhao
Journal of Medical Virology.2022; 94(2): 616. CrossRef - Assessment of potential infectivity of human norovirus in the traditional Korean salted clam product “Jogaejeotgal” by floating electrode-dielectric barrier discharge plasma
Eun Bi Jeon, Man-Seok Choi, Ji Yoon Kim, Eun Ha Choi, Jun Sup Lim, Jinsung Choi, Kwang Soo Ha, Ji Young Kwon, Sang Hyeon Jeong, Shin Young Park
Food Research International.2021; 141: 110107. CrossRef - Characterizing the effects of thermal treatment on human norovirus GII.4 viability using propidium monoazide combined with RT-qPCR and quality assessments in mussels
Eun Bi Jeon, Man-Seok Choi, Ji Yoon Kim, Kwang Soo Ha, Ji Young Kwon, Sung Hyeon Jeong, Hee Jung Lee, Yeoun Joong Jung, Ji-Hyoung Ha, Shin Young Park
Food Control.2020; 109: 106954. CrossRef - Molecular epidemiology of genogroup II norovirus infections in acute gastroenteritis patients during 2014–2016 in Pudong New Area, Shanghai, China
Caoyi Xue, Lifeng Pan, Weiping Zhu, Yuanping Wang, Huiqin Fu, Chang Cui, Lan Lu, Sun Qiao, Biao Xu
Gut Pathogens.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Review: Epidemiological evidence of groundwater contribution to global enteric disease, 1948–2015
Heather M. Murphy, Morgan D. Prioleau, Mark A. Borchardt, Paul D. Hynds
Hydrogeology Journal.2017; 25(4): 981. CrossRef - Change in Concentrations of Human Norovirus and Male-Specific Coliphage under Various Temperatures, Salinities, and pH Levels in Seawater
Poong Ho Kim, Yong Soo Park, Kunbawui Park, Ji Young Kwon, Hong Sik Yu, Hee Jung Lee, Ji Hoe Kim, Tae Seek Lee
Korean Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences.2016; 49(4): 454. CrossRef - Norovirus outbreaks occurred in different settings in the Republic of Korea
Hae-Wol Cho, Chaeshin Chu
Osong Public Health and Research Perspectives.2015; 6(5): 281. CrossRef
- A systematic review and meta-analysis indicates a substantial burden of human noroviruses in shellfish worldwide, with GII.4 and GII.2 being the predominant genotypes
- Epidemics of Norovirus GII.4 Variant in Outbreak Cases in Korea, 2004–2012
- Sunyoung Jung, Hyun Ju Jeong, Bo-Mi Hwang, Cheon-Kwon Yoo, Gyung Tae Chung, Hyesook Jeong, Yeon-Ho Kang, Deog-Yong Lee
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2015;6(5):318-321. Published online October 31, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2015.10.002
- 3,013 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Norovirus GII.4 is recognized as a worldwide cause of nonbacterial outbreaks. In particular, the GII.4 variant occurs every 2–3 years according to antigenic variation. The aim of our study was to identify GII.4 variants in outbreaks in Korea during 2004–2012. Partial VP1 sequence of norovirus GII.4-related outbreaks during 2004–2012 was analyzed. The partial VP1 sequence was detected with reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, seminested polymerase chain reaction, and nucleotide sequence of 312-314 base pairs for phylogenetic comparison. Nine variants emerged in outbreaks, with the Sydney variant showing predominance recently. This predominance may persist for at least 3 years, although new variants may appear in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Trends for Syndromic Surveillance of Norovirus in Emergency Department Data Based on Chief Complaints
Soyeoun Kim, Sohee Kim, Bo Youl Choi, Boyoung Park
The Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Genotypic and Epidemiological Trends of Acute Gastroenteritis Associated with Noroviruses in China from 2006 to 2016
Shu-Wen Qin, Ta-Chien Chan, Jian Cai, Na Zhao, Zi-Ping Miao, Yi-Juan Chen, She-Lan Liu
International Journal of Environmental Research an.2017; 14(11): 1341. CrossRef
- Trends for Syndromic Surveillance of Norovirus in Emergency Department Data Based on Chief Complaints
- Availability of Clean Tap Water and Medical Services Prevents the Incidence of Typhoid Fever
- Deog-Yong Lee, Esther Lee, HyeMin Park, SeongHan Kim
- Osong Public Health Res Perspect. 2013;4(2):68-71. Published online April 30, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrp.2013.03.005
- 3,119 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Objective:
In this study, the factors that induced a decrease in the incidence of typhoid fever were analyzed. Based on the study results, we propose a quantitative and concrete solution to reduce the incidence of typhoid fever.
Methods
We analyzed the incidence and fatality rate of typhoid fever in Korea. Tap water service rate and the number of pharmacies, which affect the incidence rate of typhoid fever, were used as environmental factors.
Results
To prevent typhoid fever in the community, it is necessary to provide clean tap water service to 35.5% of the population, with an individual requiring 173 L of clean water daily. Appropriate access to clean water (51% service coverage, 307 L) helped the population to maintain individual hygiene and food safety practices, which brought about a decrease in the incidence of typhoid fever, and subsequently a decrease in fatality rate, which was achieved twice. During the 8-year study period, the fatality rate decreased to 1% when the population has access to proper medical service.
Conclusion
The fatality rate was primarily affected by the availability of medical services as well as by the incidence of typhoid fever. However, an analysis of the study results showed that the incidence of typhoid fever was affected only by the availability of clean water through the tap water system. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- TIPICO X: report of the 10th interactive infectious disease workshop on infectious diseases and vaccines
Irene Rivero-Calle, Jose Gómez-Rial, Louis Bont, Bradford D. Gessner, Melvin Kohn, Ron Dagan, Daniel C. Payne, Laia Bruni, Andrew J. Pollard, Adolfo García-Sastre, Denise L. Faustman, Albert Osterhaus, Robb Butler, Francisco Giménez Sánchez, Francisco Álv
Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics.2021; 17(3): 759. CrossRef - Progress in the overall understanding of typhoid fever: implications for vaccine development
Peter J O’Reilly, Dikshya Pant, Mila Shakya, Buddha Basnyat, Andrew J Pollard
Expert Review of Vaccines.2020; 19(4): 367. CrossRef
- TIPICO X: report of the 10th interactive infectious disease workshop on infectious diseases and vaccines



 First
First Prev
Prev


